Physics: Energy, Fields, & Matter
Vibrations and waves
Vibration implies an oscillation which is a back and forth motion like a vibrating reed or a sloshing fluid in a container. A wave or doesn’t imply oscillation, unless it is reflected as an echo or with a mirror.
Vibration means the Rate of interchange of particles and space between its core and particles around the core. Related to volume... Slow cool ... Fast heat or burn...
Vibration result from the interaction of particles which move from vibrations of the table and from a distance look like waves, but close up look like random jumping particles.
Sound vibrations and four different colors of sand interacting
Waves. When motion of a particle is said to travel in waves and is illustrated and compared to waves which are a collection of particles, it is an over simplification in multiple ways.
First, water/smoke, ... waves don’t exist as what we interpret as one wave after another, but is composed of a collective animation of interacting particles. Therefore, what we see is the collective particles in motion interacting with other particles, which must be explained with the collectively action of the particles. Which is often overlooked as an explanation with the use of our invented term, waves.
Second, the interaction of water particles and other substances floating, suspended, or sunk in water is explained with Newtonian physics on a (10-4) or larger scale. However, photons, electrons, ... All subatomic particles interact with an Einsteiniam physics on a (10-5) or smaller scale.
What we see as light and heat are reproduced, transferred, recreated, changes form, ... by the interactions of energy. Energy that leaves the sun and is reproduced on Earth when it reaches and interacts with particles on Earth or in its atmosphere.
Particles that produce heat and light generally do not leave the sun. It is energy in forms of radiation, waves, spirals, ...
Lens compresses, focus ... energy... (doesn’t multiply)
Powerful vertices, vortex, spiral,
Time
If electrons traveled at light speed, they would think they arrived at their destination when they left their point of origin. (Like photons of light.)
Energy, Fields, & Matter
Humans first thoughts about matter was to wonder what it was made of and how small an individual piece of matter could get and still be the substance. The idea of matter being composed of earth, air, water, and fire; with the atom being a name given for the smallest substance that still had the properties of the substance.
Over time atoms were found to be composed of hadrons: protons, neutrons,(with an atomic mass of about one), and electrons. With the protons and neutrons located in the nucleus, together called nucleons. The nucleus is surrounded by a swarm of electrons. All together they make an atom, with a diameter of about 10-8 cm.
The total average number of protons and neutrons is the atomic mass, with each element having different mass numbers, based on the number of protons. Since the number of protons determines the kind of element, the atomic number and mass is unique for each each element. Also since the average electrical charge of an element is neutral, the atomic number also represents the average number of electrons.
However, not all nucleons (nuclei) of an element have the same number of neutrons. As the number of protons increase for different elements, the number of neutrons increases a few more than the number of protons increase. This results in atoms with the same number of protons sometimes having slightly different numbers of neutrons, which make different atomic masses for different varieties of the same elements, known as isotopes. For example: fluorine has one isotope and tin has ten with most having at least two.
This creates two values: the atomic number, which is always a whole number representing the number of protons in an element and atomic mass, which ranges from slightly more than double the atomic number to slightly more than 2.5 times. The atomic mass or weight is calculated from the average of large amounts of an element found in nature, which will include its isotopes. Because of the different isotopes the atomic mass is slightly more than twice the atomic number (the number of protons).
Matter vibrates
Fields are everywhere and act like liquids as ripples and waves. When a wave is formed a particle is created.
Electromagnetic force as quantum fields - quantum electrodynamics (QED). Ripples in one field can create ripples in another field.
Conservation of energy
Nature, back to nature, balance of nature, harmony of nature Unlimited abundance
Free energy technologies may be $ free, cheep, or inexpensive, However, energy is always conserved so not physics free. For example a refrigerator using power connected to the grid will cost money for the electricity. The same frig could be powered off the grid with solar panels, not cost money beyond the cost of the equipment. Or a Zero pot cooler could chill fruit and veggies without electricity. However, all three will transfer the same amount of heat energy if each are to maintain the fruit and veggies at the same temperature for the same length of time.
Resources about Particles
- A good source
- Article - Probing the frontiers of particle physics
- The Particle Adventure - Electronic book.
Standard model (SM) of particle physics
Standard model (SM) of particle physics is based on the idea that each particle is an excited state of a corresponding field and the force between them.
A force field arises when a third particle is exchanged. It fails to explain some observations: dark matter, dark energy, how atoms survived the Big Band, value of the cosmological constant (lamda = 2.036 * 10 -35 s-2), ...
Cosmological constant was created by Einstein when he thought the Universe was not expanding.
Matter and antimatter particles -
Matter - antimatter asymmetry requires forces that change strength when matter and antimatter particles are interchanged (an operation called conjugation C) with their mirror image particle (called parity transformation P) known as conjugation parity (CP). These forces violate CP symmetry in the standard model (SM) model. To preserve total symmetry CP is said to violate time-reversal (T) symmetry so that CPT is preserved.
The electron electric dipole moment (EDM) is an intrinsic property of an electron such that the potential energy is linearly related to the strength of the electric field. An electron's EDM must be collinear with the direction of the electron's magnetic moment (spin).
Within the SM of elementary particle physics, such a dipole is predicted to be non-zero but very small, at most 10−38 e·cm, where e stands for the elementary charge. The existence of a non-zero electron electric dipole moment would imply a violation of both P (parity) and T (time reversal).
In the SM, the electron EDM arises from the CP violation components of the CKM matrix. The moment is very small because the CP violation involves quarks, not electrons directly, so it can only arise by quantum processes where virtual quarks are created, interact with the electron, and then are annihilated.
Magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current.
An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges.
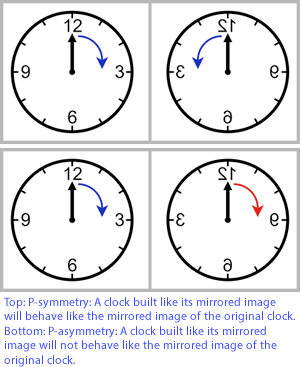
A chiral phenomenon is not identical to its mirror image (asymmetric). Hands - left and right are chiral because they are mirror images of each other, but however you reorient them, you will not be able to make them overlap.
- The spin of a particle may be used to define its handedness or helicity.
- Massless particles have the same spin and chirality.
- A symmetry transformation between the two is called parity.
- Invariance under parity according to Fermi–Dirac statistics is called chiral symmetry.
- Chien-Shiung Wu in 1957 demonstrated that parity is not a symmetry of the universe.
Forces, fields & matter
Four fundamental forces and their fields. Elementary bosons - follow the Bose–Einstein statistics - spins are integers. They transmit forces that function as glue, may stick together, can occupy the same quantum state.
- Strong nuclear force gluon fields is on a smaller scale (< less than 0.8 fm, radius of a nucleon) is the force carried by gluons that holds quarks together to form protons, neutrons, and other hadron particles. Gluon has spin 1 the nuclear force or color force.
Source shows nice animation of particles - Weak nuclear force W± and Z fields cause radioactive decay. W± and Z bosons carry the weak force and have spin 1.
- Gravity warps space time, force between masses, gravity waves, ripple space time. Missing from the SM. Graviton has spin 2. Gravitons [predicted] carry the gravity force.
- Electromagnetism photon field carry the electric and magnetic fields. Photon has spin 1 and are particles of light. Light is an electromagnetic wave. Photons - can boost electron levels up and down energy. W1, W2, W3, and B bosons carry the electroweak force and have spin 1. When the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces, the W1, W2, W3, B, and Higgs remix to make W±, Z, photon, and Higgs.
* Higgs boson. (spin 0) The Higgs boson is an excitation of the Higgs field. The Higgs field gives particles of matter and the W & Z bosons their inertial mass, but not massless particles like the photon.
Matter
Fermion - particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. They have half-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, ... ). Electron, proton, leptons, quarks, ... There are 12 types of elementary fermions - 6 quarks and 6 leptons
Elementary fermions
1. Quarks - have color symmetry and a spin of 1/2. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom are made of quarks. There are six types or "flavors" of quarks:
- up-type quarks (up, charm, top)
- down-type quarks (down, strange, bottom)
- Each comes in three colors - charges: red, green, and blue.
Leptons. (spin 1/2)
2. Electron and its two super massive sisters - muon and tau. Atoms have a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Electron - electrical charged - drive life. Electrons can cascade up and down. when cascade down they give off energy and sometimes When an electron cascades down it can pull up an electron (flavin). Electrons interact with matter about 10 000 times stronger than x-rays.
- Muon - 200 electron masses. Muon g-2 (muon gee minus two) experiment found each muon is charged (like a little bar magnet) and will circle a magnetic field. If a muon enters a magnetic field in a perpendicular orientation it will precess like a compass needle. Theory suggests if a muon is polarized in the direction it travels it locks their will in orbit. However, the muon continually emits and reabsorbs other particles (pop into and out of existence) which increases the muon’s magnetism and will precess faster than it circulates. It can emit and reabsorb any particle and the change in magnetism can signal the particle. Positively charged muons decay into positrons spit out in the direction of the muon’s polarization. Therefore, can track muons by detecting positrons.
3. Neutrinos, the electron neutrino, muon neutrino, and tau neutrino. Lightweight and weakly interacting.
Composite particles and more
Composite particles - hadrons - composed of other particles. Hadrons are made of quarks and therefore are not fundamental.
Neutron - will decompose into a proton + electron + neutrino
Protons positive charged, radius = 10 -15m Proton, gluon, quark - Three quarks are held together with gluons to make a proton.
Beta decay - two types when a nucleus has either too many protons or neutrons
- + beta decay when a proton in a parent nucleus decays into a neutron that remains in the daughter nucleus, and the nucleus emits a neutrino and a positron (a positive particle like an ordinary electron in mass but with opposite charge).
- - beta decay a neutron decomposes to a proton + electron + neutrino
Baryons. (spin 1/2, 3/2) Baryons are fermions composed of three quarks. The most important baryons are the two nucleons: the proton (up-up-down quarks) and the neutron (up-down-down quarks). Some other baryons are the sigma, lambda, xi, delta, and omega-minus.
Mesons. (spin 0, 1) Mesons are bosons composed of a quark and antiquark. Some mesons are the pion, kaon, eta, rho, omega, and phi.
Antiparticles. All particles have a corresponding anti-particle that is identical in many ways but opposite in others; for example, the mass and spin are the same but the charge is opposite. An uncharged particle may be its own anti-particle.
Quasi-particles and other non-particles
Many quantized states are not real particles, but are conveniently named and treated as if they were real particles. Some are the quantized modes of collections of particles.
- Soliton. A stable solitary wave packet arising from a combination of waves. Solitons are found in many physical phenomena, large and small.
- Phonon. A quantized sound wave.
- Electron hole. The absence of a negatively-charged electron in a semiconductor, treated as if it were a positively-charged particle.
- Cooper pair. A pair of electrons (fermions) in a superconductor, treated like a single boson.
- Exciton. A bound state of an electron and an electron hole.
- Magnon. A quantized spin wave.
- Plasmon. A quantized plasma oscillation.
- Polaron. A quantized polarization field.
Dark energy matter grows with space
Bose Einstein condensate - single quantum wave 1924.
Super partner = super symmetry = link between bosons and fermions that make up matter. Hypothetical partners - Every standard particle may have a superpartner particle: a fermion for each boson and a boson for each fermion
Elements - Noble gases (monatomic) He, N, Ar, Kr, Xe, Ra