Respiratory system review key
Describe the respiratory system.
The respiratory system primarily exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide through the lungs to provide oxygen to metabolize food, which provides energy to move muscles, repair cells, feed brains, calm nerves, and clean the body of toxins.
Describe functions of the respiratory system.
- Brings air into the lungs through the nose, mouth, and the trachea to provide oxygen to metabolize food and provide energy to move muscles, repair cells, feed brains, calm nerves, and clean the body of toxins.
- The nose, mouth, and the trachea filter the air with tiny hairs, cilia, to remove dust, bacteria, and viruses; warm it; and moisten it with mucus.
- Diaphragm contracts and expands, which changes the chest volume, thus causing air to flow into the lungs.
- Vocal cords (two bands of tissue) in the larynx vibrate when air passes between them causing vibrations that create sounds and speech.
- Inside the lungs in the alveoli blood is transported through the capillaries and the oxygen from the air attaches to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells and is transport it to the cells.
- Oxygenated blood travels to the cells, where the oxygen can be used by cells to metabolize food (glucose, fatty acids, proteins) in the mitochondria and provide energy (ATP, NADH ) that powers the cells. In the process carbon dioxide is released.
- Tranfer thermal energy from the body.
Three things that happen to air when it enters the nasal cavity.
- warmed
- filters dust, bacteria, viruses
- moistened
Parts and functions
Match the words in the word bank to the function and label the diagram.
- ___diaphragm ________ group of muscles that expands and contracts when you breathe.
- ___ carbon dioxide _____ waste gas that is not needed by your body.
- ___ lungs ___________ organs used for the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- ___ oxygen _________ gas needed by the human body to release energy from food.
- ___ respiratory _______ body system that allows the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- ___ larynx __________ body part that contains the voice box and vocal cords.
- ___ mucus __________ sticky substance in the nasal cavity.
- ___ pharynx ________ muscular wall behind the nose and mouth (throat) that connects to the the esophagus.
- ___ sound vibrations ___ made when air passes across the vocal cords.
- ___ blood/ hemoglobin__ transports gases to and from the cells.
- ___ energy _________ provided when oxygen is metabolized.
- ___ nose / mouth _____ where air is filtered, warmed, and moistened before entering the trachea.
- ___ sinuses _________ produce mucos.
Word bank
esophagus, trachea, sinuses, blood, nose, mouth, lungs, diaphragm, pulmonary arteries, villi, pharynx, oxygen, energy, carbon dioxide, respiratory, larynx, hemoglobin, mucus,
Label parts on the diagram
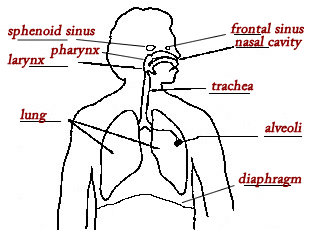
Describe ways to care for your respiratory systems.
- Don't smoke and stay away from second hand smoke. Smoke can damage the respiratory system and cause bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, and reduce the growth of the lungs.
- Eat and drink slowly and swallow while not talking so that food doesn't get into the larynx or trachea and cause a choking coughing reaction.
- Wash hands to reduce chances of infection
- Keep hands and other objects away from nose and mouth to reduce infection
- Participate in regular aerobic exercise to increase the bodies ability to use oxygen and improve health in general. See also immunity and exercise
- Avoid air pollution which can cause health problems and cancer.
Describe health related care issues
- Asthma is the inflammation and contraction of the airways (trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles) that result in difficulty breathing. Acute attacks can be treated with inhaling medication that dilates, expands, airways.
- Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs. Causes are infections and irritants like smoke, air pollution (house-dust mites, animal danders, pollens, molds, fumes from exhaust, smoke, scents from perfume, deodorants ...). Bronchi produce excessive mucus that blocks the airways, causes shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, Treatment include antibiotics and avoiding irritants.
- Colds and flu are common infections in the upper respiratory system.
- Emphysema progressively destroys the alveoli in the lungs. Symptoms include difficulty breathing and a chronic cough. Treatment can reduce symptoms, but damage is permanent. Usual cause is smoking.
- Pneumonia is the inflammation of lungs caused by bacterial or viral infection. The alveoli enlarge, clog with mucus, and decrease the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Symptoms include cough with phlegm, difficulty breathing, tiredness, fever, chills, chest pain, and dehydration. Treatment is with antibiotics.
- Sinusitis is the inflammation of the sinus cavities above the nose and throat. Can be caused by allergies, colds, flu, or other infections. Congestion, fever, stuffiness, headache are common symptoms. Treatment with nasal sprays and antibiotics.
- Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs. When infected the immune system attacks and keeps if from spreading. However, if the immune system is weakened the infection can spread and become active. Symptoms when active include coughing, fever, tiredness, and weight loss. Treatment include antibiotics, hospitalization, and rest.