Plant
Resources for teaching & learning
Questioning is the foundation of all learning.
The first step in rejecting not knowing is to ask, why?
Sweetland
Overview
- Introduction
- Planning for plant
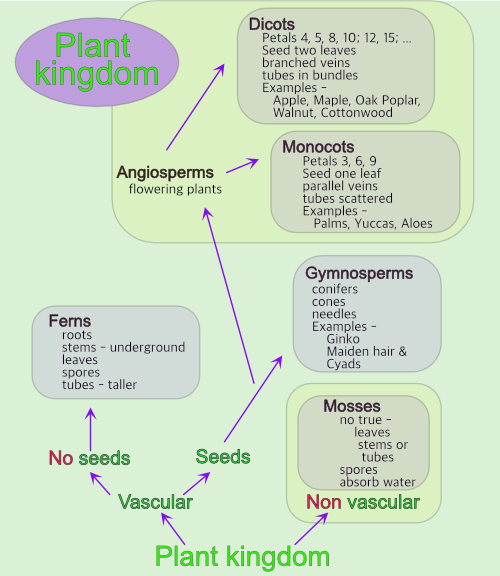
- Plant Kingdom Classifications
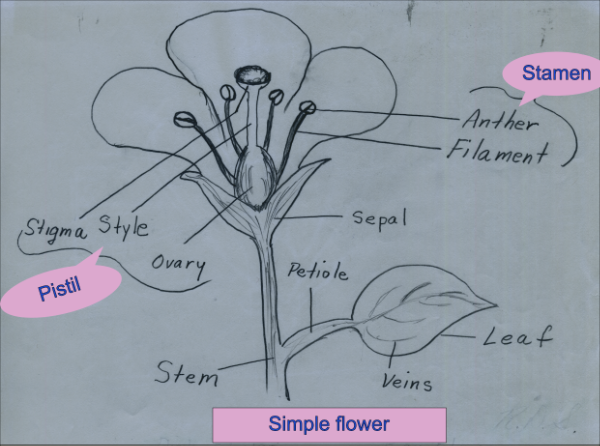
- Flowers - types, simple, compound, diagrams & photo
- Leaves -opposite, alternate, simple, compound, margins, shapes, attachments
- Fruit types
- Root types
- Trunk anatomy
- Spirals in plants - examples of Fibonacci sequence
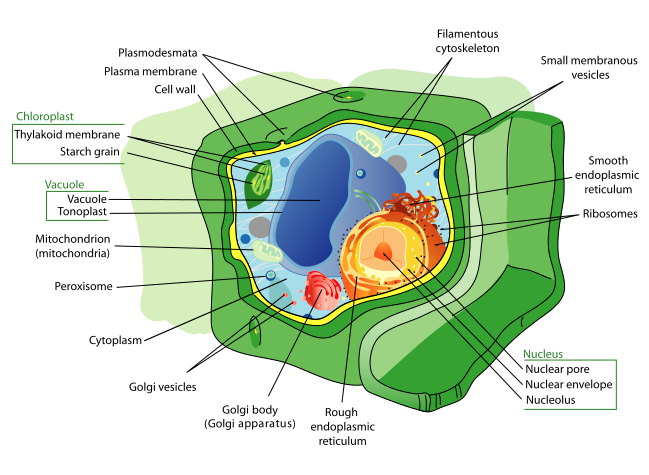
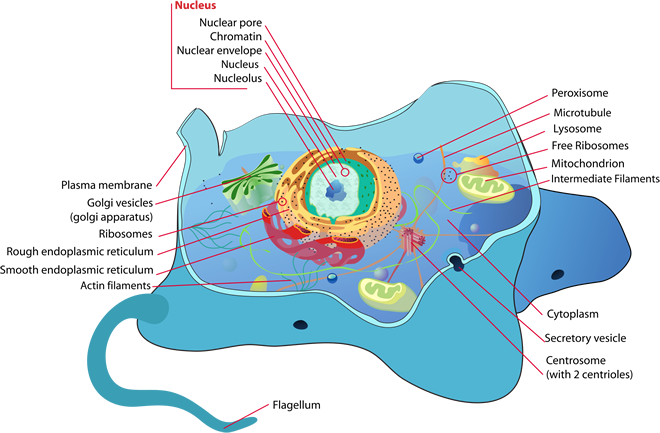
- Plant cell model diagram
- Celery & colored water activity - pictures
- How plants stay cool
- Plants and temperature
- Leaf and whole plant response to heat
- Plant assessment
- Plant and flower asssessment
Introduction
This page includes resources for teaching and learning about plants for primary and middle level learners.. Analysis of information need to construct concepts about plants in meaningful ways. Information about plants and their properties. Properties of leaves, flowers, fruit, trunk anatomy, spirals in plants, and plant cells.
Background information for planning plant activities
Information is organized into categories as in this framework and explaned here.
Created by - Courtney Maas & Jennifer Thomas
Topic - Plants
Focus question - What are characteristics of plants?
Perceptual Responses
- See - observation - location, shape, color, size
- Feel - texture, sharp, light, hard, fragile, soft, fuzzy, and smooth while others are
- Thorny and rough
- Smell - sometimes have a good smell, some not so good or bad
- Taste - can eat some plants
- Hear - leaves rustle, needle clack
Properties
- Flowering plants
- Seeds have a seed coat, embryo (baby plant) and cotyledon (stored food)
- Plants - mon cot, dicot, biennial (life cycle 2 years) perennial (life cycle 2 or more years)
- Flowers have petals, stamen, pistol, anther egg, filament
- Germination, photosynthesis,
- Bulbs
- Fruit
- Stems, twig, branch, trunk
- Leaves
- Needles - cones
- Roots
- Non Flowering plants
- Ferns - leaves, fronds, spores,
- Mosses
Relationships and concepts
- Plants are living
- Plants create energy from sun for food
- Plants reproduce
- Fruits and vegetables can grow from a plant.
- When you plant a seed in good soil, water it, and provide sunlight, a plant will grow from it.
- Plants have leaves, stems, petals, roots, flowersPlants have a life cycle
- In order to get plants, you need to have air, water, soil and sunlight.
- You plant watermelon seeds and take care of them so that they grow into watermelons. Then you can eat the watermelon.
- You plant the seeds from the watermelon you eat and grow more watermelon - life cycle of a seed.
- Do plants have feelings? Do they have senses?
- Plant Mimosa pudica seeds and after they have a second set of leaves, touch the leaves and discuss what happens.
- Venus fly plants
- Do plants need soil? gardening without soil. Grow mint seeds on sponges, move to holding trays in a hydroponic unit.
Observations
- Observe that plants can be different colors, shapes, & sizes.
- Observe all the flower parts - look, feel, taste, smell, hear.
- Observe seeds can be all different colors, shapes, & sizes.
- A bean seed is kidney shaped and white.
- Lettuce comes from a little tiny seed and tastes good.
- A rose smells good, has thorns on the stem and comes in many colors.
- Some seeds are edible and taste good and some seeds are just for making something taste better.
Transformations
- Drawing pictures of plants and label their parts.
- Make a chart and list plant parts across the top - leaf, stem, flower, root, seed, other use store and labels to classify under column
- Seed collection with labels ...Go to store - collect different plant parts, take to school, cut apart - count seeds, dry seeds, plant seeds...
- Chain story - Watch seeds grow... Draw pictures, measure growth, communicate what is happening with a chain story. When we plant a seed for sweet corn, it grows into a corn plant. We need soil, air, & sunlight for it to grow. After it grows, we can pick it and eat it. The cycle can then start all over again.
Tasks or Activities
- Hand out bean seeds for the kids to observe and talk about
- Open up a seed to see the inside. Fill out parts of a seed and chart
- Compare different types of seeds - for what purpose?
- Plant seeds and put one in the dark & one in the sunlight.
- Go on a field trip to a greenhouse to learn about different plants.
- Go on a nature walk to look at different types of flowers & plants on a nearby walking trail or in the neighborhood to explore different types of plants
- Go to a grocery store to learn about all of the different plants we can eat. - collect different plant parts take back - classify, cut apart - count seeds, dry seeds, plant seeds..
Collect different plants parts take back - classify, cut apart - count seeds, dry seeds, plant seeds... - Plant a seed
Real World Value Application
- We eat all kinds of plant parts - flowers, stems, roots, seeds, fruit,
- Plants that we eat are good for us and give use energy, vitamins, and minerals
- When you plant a garden, you can provide food for your family and friends
- Gardening is a hobby
- Flowers make your yard look pretty
- Plants can be good for the soil
- Make mulch, fertilizer
- I can understand the world
- Understanding the world gives me.... power
- Plants make our world beautiful.
Classroom atmosphere
- Hands on real life activities motivate and empower learners to explore and learn about their world.
- Working in groups to explore plants encourages cooperation; and sharing learning experiences creates positive learning experiences and positive attitudes for science and achievement.
Assessment levels
- Upper level - Plants have many different properties, but all have the ability to use energy from the sun to grow and store it for them to use and other animals to use.
- Lower level - Plants grow, but don't move from place to place.
Instructional assessment
- Learners ask questions and participate in the activities.
Plant kingdom
Flowers
Complete flower example

Flower anatomy simple
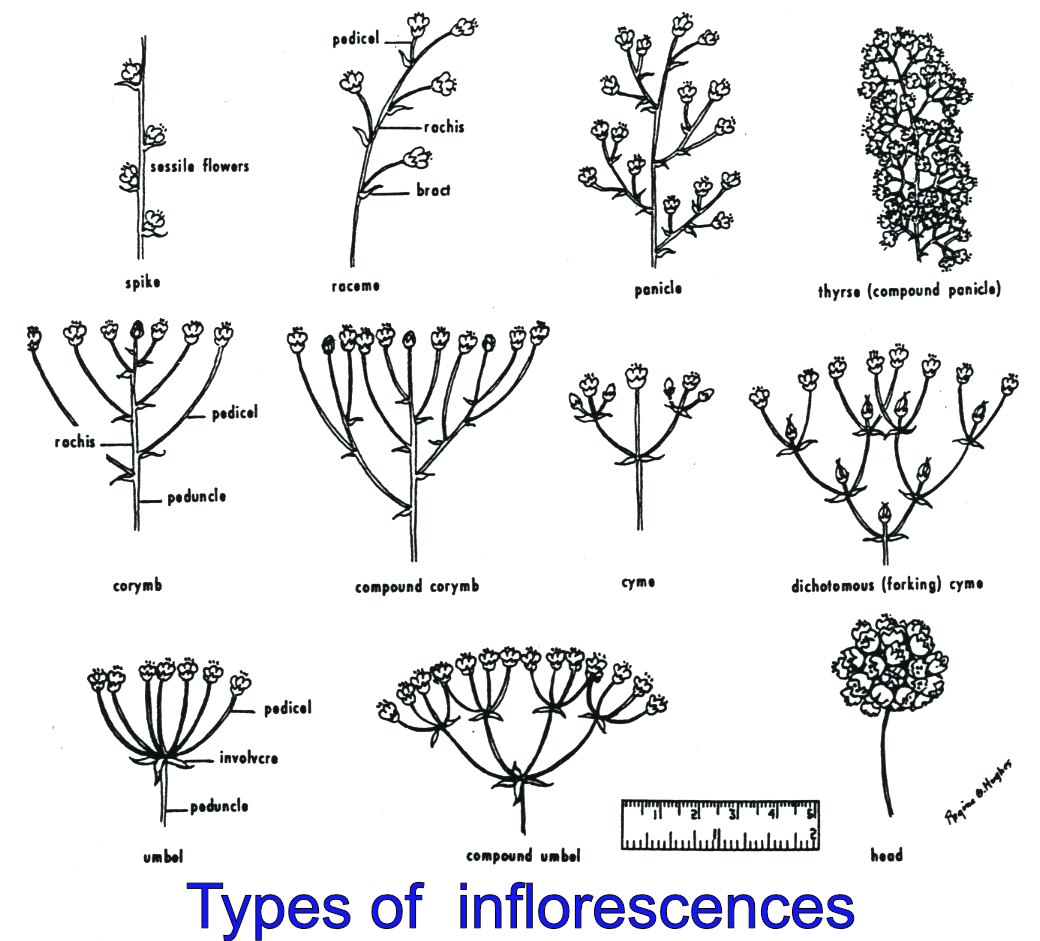
Flower anatomy compound flowers
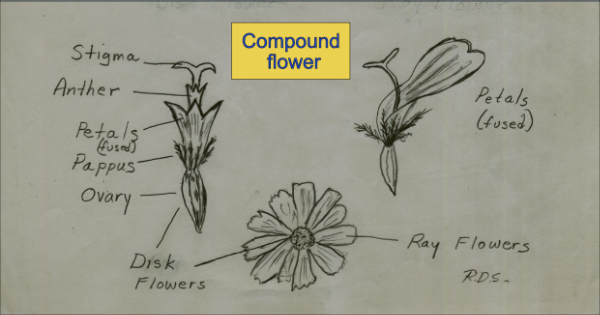
Leaf
Leaf attachment and shape
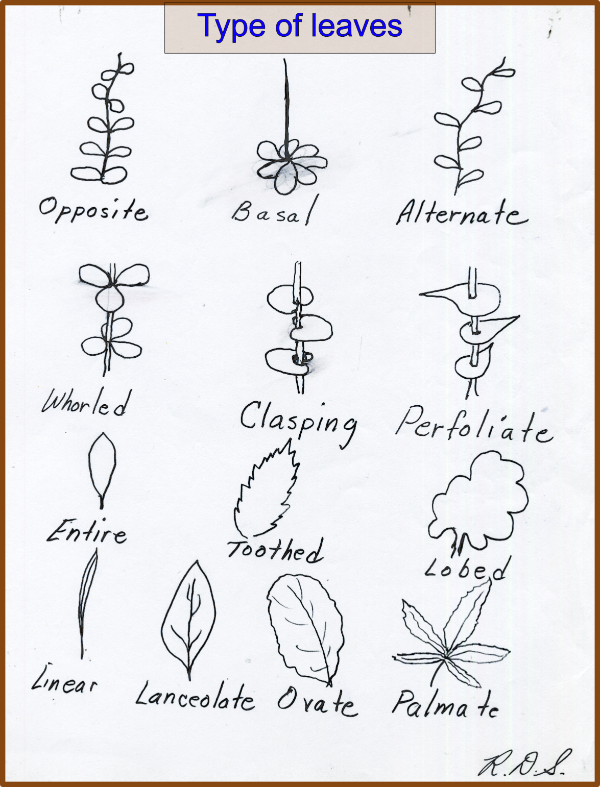
Leaf attachment & shapes
Leaf margin
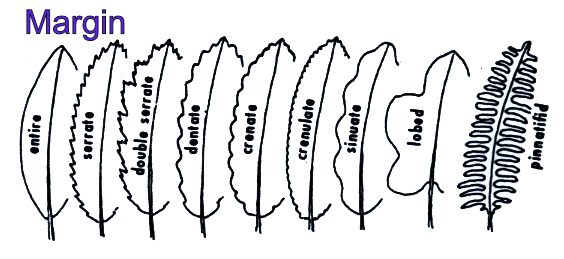
Leaf shape

Leaf attachment top

Leaf attachement bottom

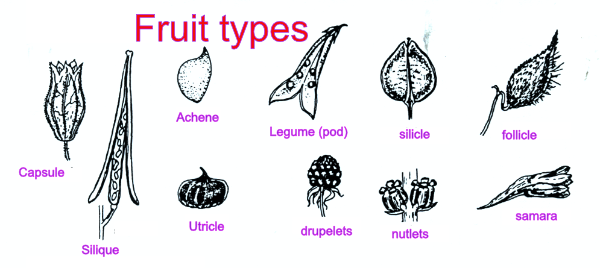
Fruit types
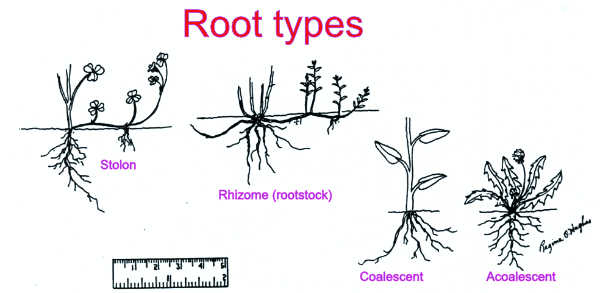
Root types
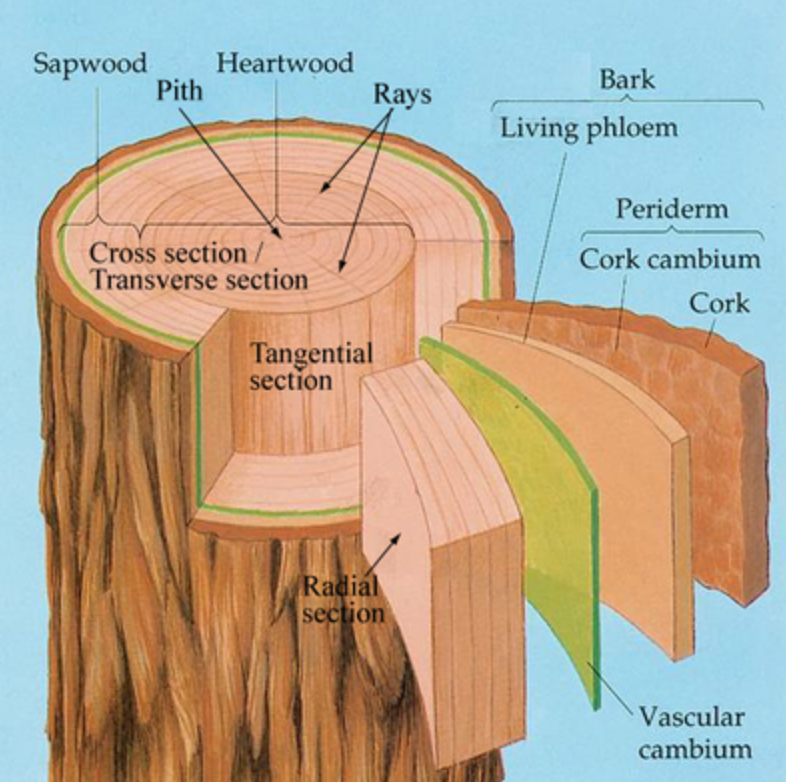
Trunk anatomy
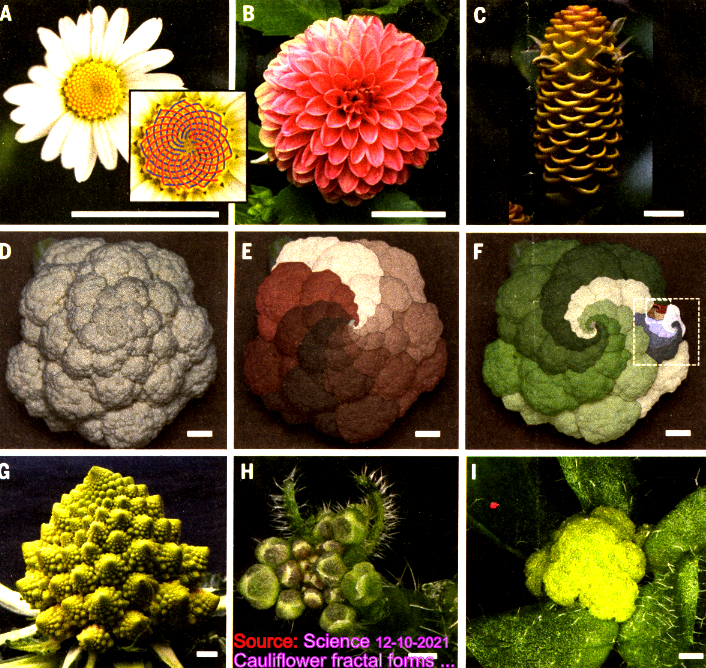
Spirals in plants examples of Fibonacci sequence

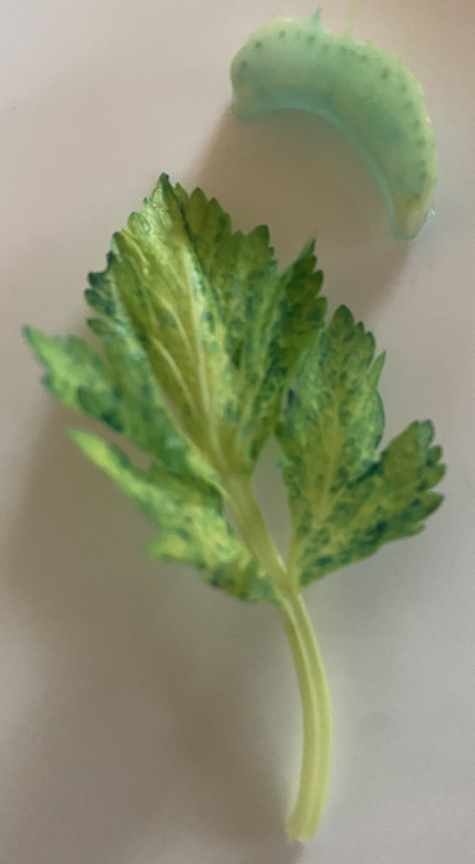
Plants & water tranportation







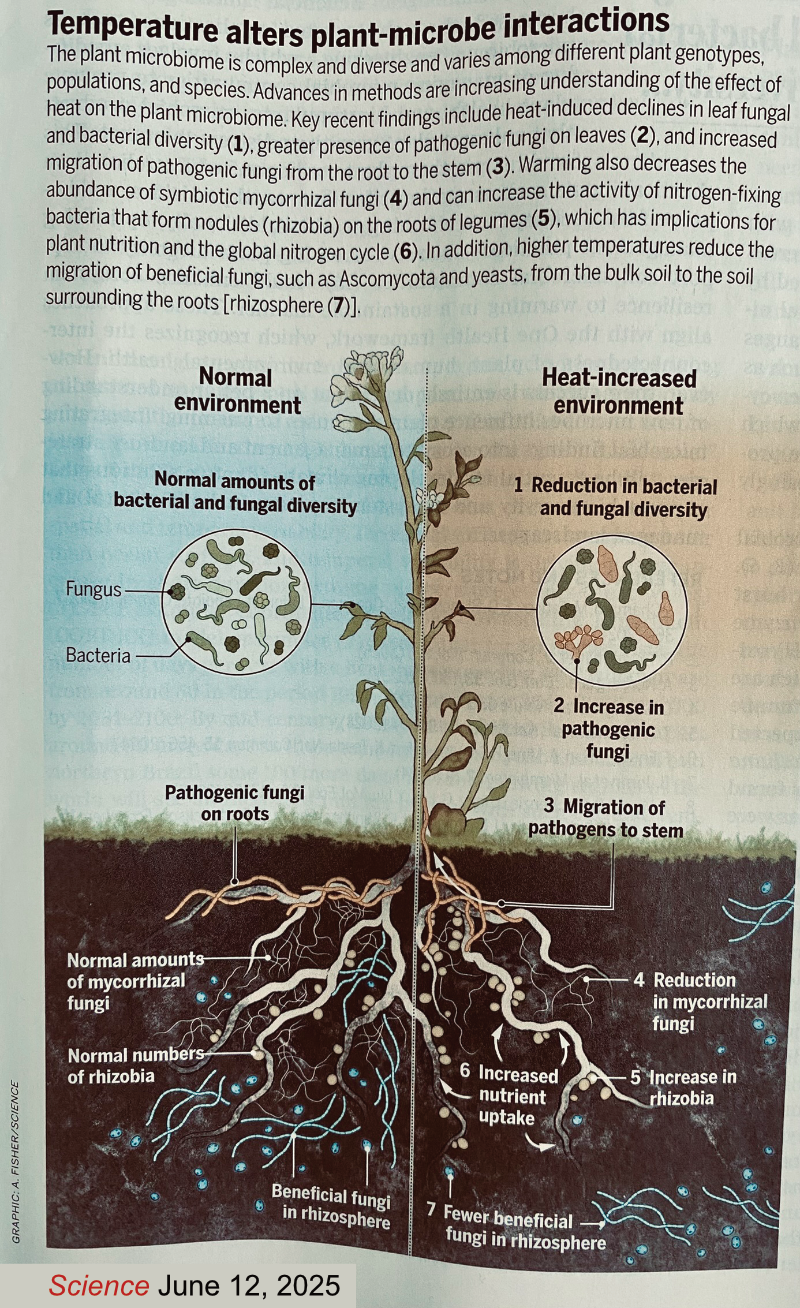
Plants & heat: Climate change
How plants stay cool.
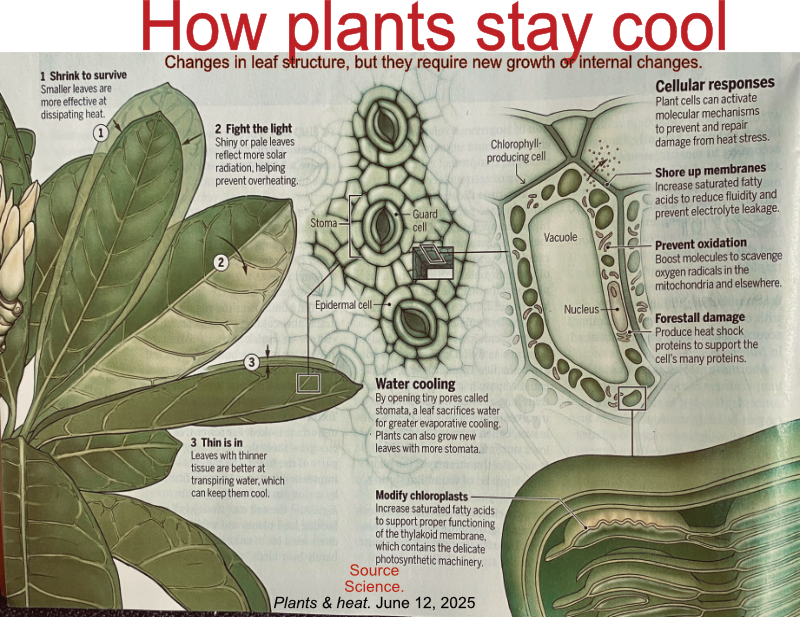
Plants and temperature - What plants can survice clinate change?
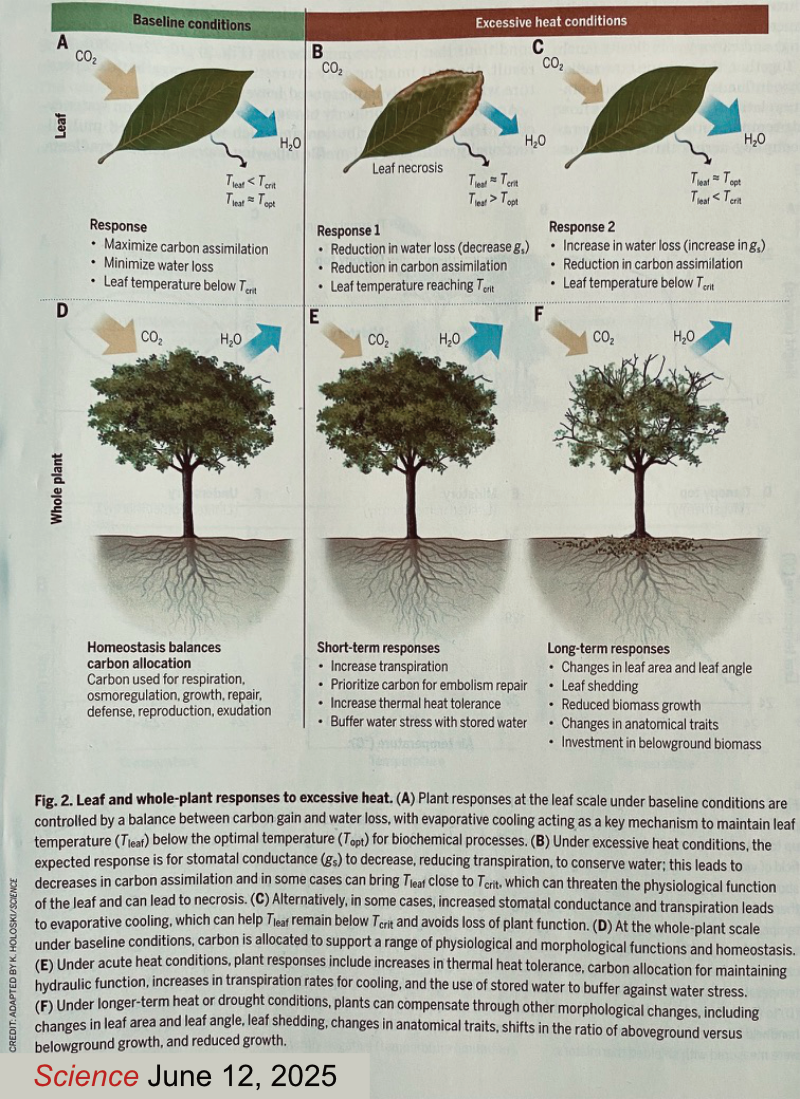
Leaf and whole plant response to heat
Plant assessment sample 1
- ____________________ All plants are divided into two large groups. What are the two groups?
- ____________________
- ____________________ What is the name of the group of pants that have tube like structures in them.
- ____________________ What is the name of the group of plants that doesn't have tube like structures in them?
- ____________________ Give an example of a nonvascular plant.
- ____________________ What is a group of plants that is vascular and has spores instead of seeds?
- ____________________ What is the name for the group of plants that has seeds, but the seeds aren't produced in an ovary?
- ____________________ What is the name of a group of plants that have seeds produced in an ovary?
- ____________________ Angiosperms can be divided into two groups, what are they?
- ____________________
- How do plants get their food?
- What is an annual?
- What is a perennial?
- ____________________ List three conditions necessary for plant growth.
- ____________________
- ____________________
- What is the difference between decidous and evergreen?
- Why is a dicot more advanced than a monocot?
- ____________________What is the name of a scientist that studies plants?
- Mosses and ferns produce new plants by forming what?
Plant- flower - assessment sample 2
- ____________________ What is the pretty part of the flower?
- ____________________ What part of the flower is often planted underground?
- ____________________ What part of the plant grows underground?
- ____________________ Where is the food made in plants?
- ____________________ What word best describes the moving of the pollen from the stamen to the pistil?
- ____________________ What word best describes the process of the sperm celljoining with the egg?
- ____________________ What word best describes the process of a seed beginning to grow?
- ____________________ What is the process of plants making food called?
- ____________________ What is the process of animals changing food to energy called?
- ____________________ What is the wearing away of soil by water or wind called?
- ____________________ List two necessary conditions for germination of seeds?
- ____________________
- ____________________ List three ways plants may be grown without seeds.
- ____________________
- ____________________
- - 23. Circle the words that have something to do with the male part of the flower.
fruit, ovary, stamen, anther, pistil, pollen, filamant, bulb
- - 32. Circle the words that have something to do with the female part of the flower.
stem, pistil, stamen, egg, stigma, style, ovary, leaf, bulb
33. - 34. Describe two ways pollination can take place.
35. - 39. Tell five different ways plants are used.
40. - 48. Circle what plants need to make food.
oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, soil. light, food, starch, sugar, blood
49. - 58. Circle what plants make or give off because of photosynthesis.
oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, soil. light, food, starch, sugar, blood
59. - 61. Circle what animals need to get energy.
water, food, oxygen
62. - 67. Circle what animals get or give off when they undergo respiration.
food, energy, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, sugar
| pollination | germination | fertilization |
| respiration | photosynthesis | reproduction |
| flower | petal | style |
| seed | stem | root |
| cuttings | bulbs | runners |
| erosion | fruit | ovary |
| stamen | anther | nectar |
| pistil | egg | stigma |
| calyx | filament | pollen |
| sperm | leaf | trunk |
| bark | twig | branch |