This page is a comprehensive source to reflect and share ways to interact with individuals and groups, both inside and outside classrooms, to use behavior analysis to manage and faciliate learning. Learning with dignity through effective communication and interactions to sustain or motivate learners who will have the self-efficacy to set and achieve goals to facilitate their growth in a sustainable community. Growth in understanding themself and learning what is necessary (social, emotional, physical mental, & intellectual) to become life long learners.
Historically this has been known as management, which people perceive in different ways. Ways, to manage, which are often described with verbs: run, organize, care, lead, control, supervise, oversee, and guide.
This list includes twelve different kinds of outcomes, which can be used to guide a reflection to select actions and goals for your managagement style of individuals, groups, and classrooms. A vision and action plan of management. For example: If you believe teacher leaders are the best way to help people achieve a life worth living, then review or create documents to describe this vision. The following information is provided to achieve this and to generally assist people to learn and grow in positive ways.
Quotes that might inspire your management ... like ...
We are all imperfect humans doing the best we can. Give warmth, affection, care, and unconditional positive regard.
Theories, Models, and Teacher tools for behaior analysis decision making
- ABC (antecedent, behavior, & consequences) - overview and suggestions to use ABC for behavior analysis of cause and consquences of behavior.
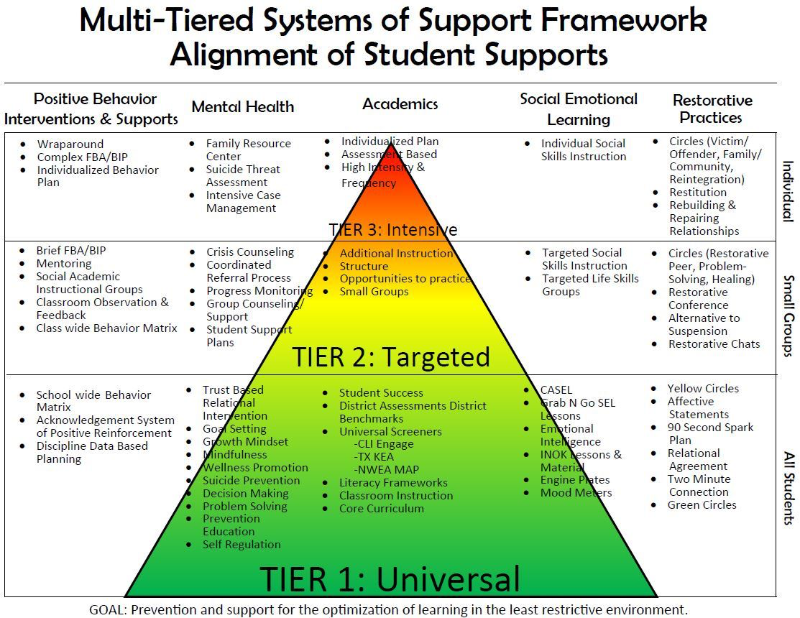
- Applied behavior analysis management intervention plan (Six Step) is a multi-tiered system of support.
- Assorted theorists - their main ideas and principal teachings for discipline & management
- Behavior management - defined, decision making screen to assist behavior change, implementing change, & fair pair rule
- Behavior forms to use in management plans: like a Six Step management plan.
- Misbehavior form - describe what happened & describe a better action for next time
- Problem solving form 1 - describe what problem interfers with, three ways to handle, make a choice, & plan of action for next time
- Problem solving form 2 - describe what problem interfers with, three ways to handle, create plan of action for next time, & describe who can help & how
- Brainstorming &
- Brainstorming solutions for problems - brainstorm problems, then select a problem, & brainstorm solutions.
- Brainstorming directions & suggestions
- Exploratory writing or rough draft
- Goal analysis form - five day plan to analize respect & cooperation & set respectful & cooperative goals for the week
- Problem report form - form for students to fill out for any problem they have
- Caring - Caring research and ideas to develop caring learners
- Rigorous evaluations show the Child Development Project (CDP) to be effective at fostering students' academic, ethical, social, and emotional development. These findings brought CDP significant national recognition.
- Overview - what is the project and why...
- Summary of the project as given at Conference Presentation
- School as a Caring Communitee - the CDP way
- Creating School Connectedness - using CDP
- Connect the Research to Practice: Information to connect CDP to literature to create caring.
- Samples of commercial CDP program By grades:
- Rigorous evaluations show the Child Development Project (CDP) to be effective at fostering students' academic, ethical, social, and emotional development. These findings brought CDP significant national recognition.
- Classroom Academic organization model - review of different ways to organize classrooms
- Classroom procedures - direct & indirect instructional models with procedures to teach
- Conflict resolution, problem solving, and mediation - article with procedures, strategies, resources, & more
- Collaboration, cooperation, social skills, communication, and discourse development
- Collaboration, cooperation, social learning theory, & social skills - benefits; social theory; supporting research; 50 pro social skills by category; looks like, sounds like, & feels like charts for social skills, suggestions for collaboration & subskills, 15 sample scenarios to discuss & decide what social skills might be necessary to be successful & links to related topics
- Groups and group management
- Role Play & Role Reversal: Steps and Suggestions
- Building a school community with Child Development Project CDP
- Equity Maps - an application to chart verbal interactions in groups.
- Cooperative learning & teaching - overview of cooperative learning as an instructional model: comparison to individual & competitive models, benefits, five elements, six step plan lesson plan framework, sample lesson, planning checklist, strategies, & group processing suggestions
- Social health & relationships - instructional unit with activities & support materials
- Team building
- Classroom as a positive social environment - includes characteristics of a - traditional classroom social environment
- Boy's Town interventions and SODAS

- Culture and Black Americans
- Culture and Native American Daughters
- Ethical Issues - necessary to consider when making behavioral change decisions
- Environmental classroom considerations
- Field Trip procedures and planning guide
- Help, forgive and forget, punish, or get even?
- Holistic behavior theory or model includes:
- Six historical theories for the causes of behavior with a summary for each model, related methods of diagnosis, goals of intervention, intervention strategies, key terms, & notable names associated with each theory.
- Case studies that investigate each historical theory, explains causes of behavior, & how different theories affect intervention choices & outcomes
- Conversational influences on behavior & how to use to them to change behaviors: Article & resourcess including five step Hueristic flow chart
- Conflict resolution, mediation, social problem solving, violence programs: Article & resources
- Cooperative learning article & resources
- Goal setting unit - in health curriculum - includes Goal setting steps
- Decision Making, Critical Thinking, and Change Processes: Article & resources
- Reinforcement, punishment, and behavior change: Article & resources
- Verbal interactions - Describes different types and how to use them within conversations
- Case studies to investigating historical theories to explain causes of behavior & how different theories affect intervention choices & outcomes
Laws & legal issues
- Notes and discussion related to legal issues
- Nebraska Student Discipline Act: Nebraska Council of School Administrators Revised, 1997
- Regulations and standards for special education: Nebraska Department of Education RULE 51 effective July 15, 2014 (revised)
- School health and safety regulations: Nebraska Department of Education RULE 59 includes rules for dispensing medicine at school
- Leadership model - control from laise-faire to autocratic
- Maladaptive behaviors | intervention chart | self-fulfilling cycle |
Motivation & reinforcement
- Motivational theory, Self-Efficacy, and Attribute theory
- Maladaptive behaviors: includes interventionchart and self-prophecy cycle
- Reinforcement, punishment, and behavior change
- Glasser notes
- Teacher's actions to facilitate responsible behaviors
- Misbehavior levels and interventions
- Moral & ethical - theory, development, teaching, & instruction notes
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs
- Research on the motivation of - out of school interventions & after school care to promote mastery behaviors
- Pedagogy (model of teaching and learning)
- Physical health. Resources include activities and support materials.
- Mental & emotional health. Resources include activities and support materials.
- Multi-Disciplinary teams (MDT) procedure and timeline
- Safety and children: What every child should know to feel safe
- Student Assistance Teams (SAT) procedure and timeline
- Verbal interactions
Getting to know learners and building social cohesion
- First Day of School notes
- Socio grams
- Icebreakers, interviews, interest finders, & surveys
When giving directions for an icebreaker activity consider the inclusion of a step where the listeners are asked to make a follow-up comment or question after each person shares their response. Doing so will improve listening and the attention given to those who are sharing. - Team Building and social cohesion activities - see Collaboration ...
- End of year memories letter
Parent and community relations
- Parent teacher conference outline guide
- Parent teacher student conference form
- Parent and community involvement for student learning
- Sample letters to students and parents
Recess - Recess isn’t recess if it isn’t free choice.
Social skills - Collaboration, cooperation, social skills, communication, and discourse development
Student's their thoughts and words
- About respect and disrespect
- About low self-esteem and self-efficacy
- Assessment of teacher
- Capable people
- Speakers classroom suggestions and procedures in class
- Stress -
- System wide Discipline System Procedure
- Syllabus suggestions & checklist for making a syllabus
- Videos, suggestions and procedures for class use

Intervention notes
These interventions, as well as others, can be used in procedures for helping ourself and others to change behavior. It is through interacting as learners to set goals, create a plan, and implement interventions that we achieve mastery oriented behaviors.
Educators with pedagogical and management skills can intervene with a general conversational procedure to facilitate change by incorporating any of these interventions individually or in combination. Intervention for environmental change, self-monitoring, social reinforcers, stimulus control, extrinsic reinforcement, response cost ... along with appropriate verbal interactions.
Background
Some possible indicators for interventions as they can causes student's to struggle and lead to absenteeism and possibly dropping out if solutions aren't found.
- Academics are so challenging that students fail to attempt to work or complete assignments in a manner that motivates them to learn how to learn.
- Are disconnected or disengaged as learners or with their peers.
- Are chronic discipline problems.
- Lack school resources and supports.
- Technology and social media interfers with their learning or positive social interactions.
- Has or is developing a history of chronic absenteeism and truancy.
- Bullying.
- Has power issues.
- Involved in school violence.
- Has a history of family mental and/or physical health issues.
- Involved with negative peer influences.
- Has substance abuse issues.
- There are language barriers.
- There are cultural and racial disparity.
- Homelessness.
- Poverty.
- Pregnancy.
- Lack of grit and fostering resiliency and a self-encouraging mindset.
- Are unable to meet their needs for appropriate personal choice and freedom.
All interventions should be implemented in an ethical manner and use the fair-pair rule.
Interventions should be selected which are the least restrictive and have the greatest opportunity for success.
Least restrictive interventions require self-discipline and intrinsic motivation for students to cooperate and learn, which further increases self-discipline, intrinsic motivation, and self-efficacy.
Most restrictive interventions use extrinsic motivation and are often used with students that lack self-discipline. These interventions alone seldom help students develop self-discipline, intrinsic motivation, and self-efficacy. Hence they are best paired with other interventions.
Stages of misbehavior descriptions and interventions
Intervention strategies below are categorized into six categories in a continuum from least restrictive to most restrictive.
Intervention strategies
Environmental interventions - least restrictive
- Environmental Management and instructional suggestions
- Team building activities
- Role Play steps & role play reversal | Sample role play and steps |
- Talk around the issue
- Community involvement
- I-statements & other verbal interactions.
- Everyday conversations to get to know students, talk to them individually, communicate in multiple ways, provide sufficient feedback and feedforward about their progress academically, socially, and emotionally, if there is a need to provide corrective information, always it privately.
- General conversational procedure to help students change along with appropriate verbal interactions.
- Motivational Theory notes and procedures for achieving Self-Efficacy, self regulation, and achieving goals
- Motivational interventions
- Interest boosting - relate interest of your or others, model enthusiasm for the activity or topic, video clips of others enjoying the activity, short motivational phrases, stories...
- Hurdle help - for students that don't get started right away. Complete the beginning of the assignment together, help students find a topic, book, start an outline, talk about possible ideas for study, ...
- Support from routine - remind students about the routine or procedure and tell them to get started and see how it goes and if they need help, then let you know and you will deal with it together then.
- Fair pair rule
- Good teaching practices
- Good pace of lesson - move things along, don't belabor or dwell on anything, keep students on the clock, and always look forward.
- Developmentally appropriate activities
- Consistent routines
- Motivational activities and tasks
- Shared responsibility and choice
See also stimulus control below:
- Materials and space management as environmental management
- Variety of materials
- Comfortable room
- Encouragement
- Caring for students in school
- Grouping selecting, assigning, and managing groups
- Socio gram
- Social skills - Collaboration, cooperation, social skills, communication, and discourse development
- Transitions from activity to activity and good student movement
- Humor & sarcasm as behavioral intervention
- Level system as a strategy for shaping behavior
Self monitoring strategies to manage tension, stress, anxiety, annoyance, giving up
- Social skills - Collaboration, cooperation, social skills, communication, and discourse development
- Body language, nonverbal communication, & power poses. See: TED talk. Your body language shapes who you are. by Amy Cuddy. Amy describes examples supported by research for the effects of powerful and low power body language on the judgement & consequences of interactions with others and the health effects on the body: changes in testosterone & cortisol amounts. 2012, (21:02).
- Self talk
- Goal setting
- Decision making, Critical Thinking, and Change Processes
- Conflict resolution
- Problem solving strategies
- Problem solving rug
- Peace formulas
- Study skills
- Group skills
- Classroom meetings general and specific problem solving
- Bibliotheraphy Literature for caring
Social reinforcers
- Specific and general praise- written, oral, nonverbal
- High 5, Happy notes, Pat on back, Tell someone else how you feel about being successful, Wink, Sufficient feedback and feedforward, Post good work, Secret sign, Handshake, Thumbs up, Notes to students, Notes to parents
- To manage student talking appropriately
- Classroom meetings
- Classroom social contract, rules, and code of conduct
- Student of the week
- Encouragement
- Appeal to pride
- Social skills - Collaboration, cooperation, social skills, communication, and discourse development
Stimulus Control
- Contingencies: Can be written or oral. They are basically: If, then and When, then statements. Also know as: Grandma’s Rule or Premeck’s principle:
Eat your beans and you can have dessert. When, then:
When you eat your beans, then you can have dessert. If, then:
If you eat your beans, then you can have dessert.
Could also use what is know as a reverse of If, then:
If I help you with the first one, then do you think you might be able to do the second? or
After you do the first one together with the student, then... If I help you with one more, then do you think you can do the next one? - Self-management contracts
- Countoon
- Peer-management
- Mediation
- Modeling
- Change time of activity
- Change setting of activity
- Shaping
- Prompting
- Extinction
- Proximity control
- Interest boosting
- Student centered instruction
- Move student’s desk
- Move student in class
- Antiseptic bouncing
- Use of a study carrel
- Physical guidance
Extrinsic Reinforcement
- Reinforcement
- Reinforcers
- Rewards - beans in a jar, extra recess, free time, centers by choice, film, tape, stickers, treasure chest, stars, extra free time, recess, awards‚
- Token economy
- Point system
- Contingency contracts
- Group contingencies
- Level systems
- Differential reinforcement of other behaviors (DRO)
- Differential reinforcement of alternative behaviors (DRA)
- Differential reinforcement of incompatible behaviors (DRI)
Response cost - most restrictive
- Logical consequences
- Punishment
- Rules
- Contingencies (contract individual or group)
- Remove reinforcers
- Reduce recess time,
- Take away choice time,
- Give more work,
- Fines
- Check marks on the board
- Planned ignoring
- Point system
- Overcorrection, positive practice, and negative practice
- Negative practice
- Time-out in class
- Time-out out of class
- In-school suspension
- Detention
- Out of school suspension
Activities to Practice Teacher Skills and Create documents for classrooms
Preactivities to get to know ...
- Case Studies, Scenarios, Role Plays and Simulations - 50 different scenarios to reflect & role play different ways to communicate, interactions, & behavioral interventions. Includes suggestions for long & short term.
- Confidence test with suggested procedures to build confidence
- Survey of Attitudes Toward Children (SATC)
- Teacher Variance Inventory (TVI) Calculator - an inventory used to relate consistency of beliefs and behavioral causes to behavioral management interactions and techniques used with students. Closely related to the six historical models for the causes of behavior see above.
Activities to make or build
- Applied behavior analysis behavior management intervention plan (Six Step)
- Classroom Action plans - philosophy, policies, procedures, and outcomes
- Code of conduct & classroom rules - This page defines a code of conduct. It includes information to explore three different ways, with examples for making and implementing a code of conduct and one example of making and implementing classroom rules & social contract.
- Educational purposes & philosophies
- Emergencies, school intruder
- Physical Restraint Policies & Procedures and Seclusion: A Technical Assistance Document Nebraska Department of Education Version June, 2010
- Rules & social contract - making and implementing classroom rules & social contract
Teacher resources by Labels
General information about labels
- Abuse & neglect - NE statutes and interview suggestions
- Adverse childhood experiences (ACE): abuse (physical, sexual, emotional) & neglect (physical, emotional) & household dysfunction(domestic violence, substance abuse, mental illness, divorce, separation, family member in jail)
- Anxiety, resilience, depression, suicide prevention: Medication might reduce anxiety, it might make you feel less anxious, but it might do nothing to change whatever happens in the brain as a result of life experiences that drive the anxiety & depression process.
- Partnership for resilience see resources link
- ADHD & ADD & Bipolar - notes and intervention scenarios
- Alcohol & drug abuse lesson plans & student activities
- Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by very early onset of dysfunction in social communication and interaction, repetitive behavior, and limited interest. It is believed ASD results from complex gene-environment interactions, with strong and clear genetic influences. MECP2 linked to Rett syndrome, GABRB3 - SHANK3 Phelan-McDermid syndrome, FMR1 - fragile X syndrome, CNTCAP2 Source
- Behavior policies.pdf - Nebraska State board model of behavioral policy for dress code & grooming, pregnancy & parenting, dating violence prevention
- Bully & bullying - General information Interventions and Symptoms, aggressive behavior & consequences, & NE Bully laws
- Character counts & Kindness101 digital classroom with teaching resources for character skills and SEL
- Civil rights: Protect students civil rights: anti-discrimination, sexual harassment, trans student protection, immigrant students, at NEA edjustice
- Conflict resolution
- Culture, stereotypes, race, and suggestions for cultural diversity classrooms | Poverty - Ruby Payne
- Cystic Fibrosis model
- Diabetes
- Domestic violence - Results show exposure to a disruptive peer in classes reduce math and reading test scores in secondary schools and exposure to children linked to domestic violence explains 5 percent of the rich-poor earnings gap and each year of exposure to a disruptive peer reduces the classmates' future earnings by $80,000. Source
- Down's syndrome
- Emergencies, school intruder
- Fetal alcohol Spectrum Disorder articles also [classroom suggestions]
- Fragile X - caused by the FMR1 gene on the x chromosome instructs the mRNA (the genetic blueprint for making proteins) how to binding process that creates FMRP (fragile X mental retardation protein) which are used to build proteins, some of which are used to construct nerves. Fragile X affects 1 in 2000 men and 1 in 4000 women. see autism
- Genetics & DNA, relationships of biophysical, & environmental effects & the use of DNA to make educational decisions. Heritability & Polygenic scores
- High ability
- Starter notes & outline for the video: The “In Crowd” and Social Cruelty – an ABC News Special with John Stossel
- Islamophobia Lesson/UNIT: by Fakhra Shah
- Justice - Learning for Justice (formerly Teaching Tolerance - web site with publications and classroom and teaching resources for educators and all learners to supplement curriculum and practices to create inclusive school communities; where children and youth are respected, valued and welcomed participants. Founded by the SPLC as Teaching Tolerance in 1991 to prevent the growth of hate by reducing prejudice. It has evolved as a center to assist students and educators to realize justice.
- Let's Talk: Facilitating Critical Conversations with Students - .pdf for Teaching Tolerance includes suggestions for conversations about - race, gender, Black lives matter, Whiteness, Facilitating Critical Conversations With Students
- See also - race
- Latch Key children, leaving children alone, children supervising children
- LGBTQ community - NEA Resources
- Lice | Managing Head Lice Safely (018) - No Nit Policies | UNL extension - Lancaster County Insects, spiders, lice and more... |
- Long term illness, terminal illness, suicide, and grief
- Maladaptive behaviors with intervention chart, and self-fulfilling prophecy or cycle.
- Mental and emotional health unit - for middle level and above students
- Motivational theory
- Multiple intelligences theory - reviews nine categories, explanations, examples, and discussion on how activities fit or don't fit different intelligences
- National Education Association - home page with links to resources
- Online education community - login for members and non-members to share resources
- Nervous system cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's, epilepsy, migraines, head injury, & spinal injuries
- PANS (Pediatric Acute-onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome) - is the large class of disorders and PANDAS (Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated) is one specific type association with streptococcal infections. Depending on which brain structure the immune response attacks, a range of psychiatric problems can result: OCD, hyperactivity, inattention, anxiety, restricted eating, hallucinations, or autistic behavior. See Hidden Invaders Infections can trigger immune attacks on kids’ brains, provoking devastating psychiatric disorders. By Pamela Weintraub, Wednesday, March 29, 2017.
- Neuroinflammation and psychiatric illness
- Neuropsychiatric Disorders and infection-induced autoimmune disorders - Can be identified with the Cunningham Panel. The panel measuress: Anti-Dopamine Receptor D1, Anti-Dopamine Receptor D2L, Anti-Lysoganglioside, GM1 Anti-Tubulin, & CaMKII (Calcium-dependent Calmodulin Protein Kinase II).
- Parents with horizontal identities - Andrew Solomon Far from the Trees. Andrew writes about the complexity and unexpected situations of being a parent of a child with serious medical problems, which he calls, horizontal identities. Over ten years he interviewed more than 300 families of children with, horizontal identities, a term he uses to include children with recessive genes, random mutations, prenatal influences or values and preferences that the child does not share with their parents. (deafness, dwarfism, Down's syndrome, autism, schizophrenia, multiple severe disabilities, prodigies, children conceived in rape, who become criminals, and who are transgender)
- Procedures for identification of High ability Learners - NE .pdf
- Psychopath see Child Development Project (CDP) - to maintain & develop caring relationships
- Work-inhibited students
- Race
- Culture, stereotypes, race, and suggestions for cultural diversity classrooms
- Advocating for Racial Equity in Our Schools - NEA site
- DEI - editorial in support
- Let's Talk: Facilitating Critical Conversations with Students - .pdf for Teaching Tolerance includes suggestions for conversations about - race, gender, Black lives matter, Whiteness, Facilitating Critical Conversations With Students
- Housing & schools: The importance of engagement for educators & education advocates
- Racial justice in education
- Minnesota Educator Academy’s program for Facing Inequities and Racism in Education (FIRE) - to disrupt systemic racism and racial inequities in Minnesota’s education system.
- A Conversation With Native Americans on Race - Video ( 6:23 ) By Michèle Stephenson and Brian Young.
- Reinforcement, punishment, and behavior change
- Schizophrenia relation to C4 gene
- School safety NEA sources
- School Shootings and other Traumatic Events: How to Talk to Students
- Seating in the classroom - flexible seating
- Sex and reproduction education
- Comprehensive Sex Education fact sheet
- Common questions answered by Laci Green
- Advocates for youth K-12 curriculum
- Social skills - Collaboration, cooperation, social skills, communication, and discourse development
- Student Dress code - Girls Fight Back Against Gender Bias in School Dress Codes by Brenda Álvarez.
- Suicide preveention Web site - National Suicide Prevention Lifeline whose mission is to provide immediate assistance to individuals in suicidal crisis by connecting them to the nearest available suicide prevention and mental health service provider through a toll-free telephone number: 1-800-273-TALK (8255). It is the only national suicide prevention and intervention telephone resource funded by the Federal Government.
- Teaching Tolerance now Learning for Justice
- Trauma - Teaching Children from Poverty and Trauma.pdf - A handbook with information about symptons of trauma students and stratagies to build resilience and enhance learning.
- Verbal interactions

Learning to become a better classrooms manager
- Activities & schedule - to guide learning classroom management EDU 406
- FAQ's Frequently Asked Questions of teachers about classroom management.
- Alfie Kohn blog, books ...


Studyies find:
Common Pesticides Linked to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
A study finds a connection between high exposure to common pesticides and increased risk for children developing ADHD.
Maryse Bouchard and colleagues used data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) collected from 2000 and 2004. The sample included more than 1,100 children aged between 8 and 15. In this sample 119 were diagnosed with ADHD and their urine samples contained dialkyl phosphates - chemicals which result when organophosphate pesticides used to protect fruits and vegetables are broken down by the body. In the samples with a 10-fold increase in one of those compounds, the number of children with ADHD was more than half. And for the most common breakdown product, dimethyl triophosphate, the odds of ADHD almost doubled in kids with above-average levels compared to those without detectable levels [Reuters].
There are about 40 organophosphate pesticides in use in the United States, the most famous is malathion. In 2008, a government report found detectable concentrations of malathion in 28 percent of frozen blueberry samples, 25 percent of fresh strawberry samples and 19 percent of celery samples [MSNBC].
The weakness of their study is the NHANES data use only one urine sample. Thus, they couldn’t determine the source of contamination, nor could they see how levels of the chemicals in question built up over time. As such - Bouchard and colleagues write, their study shows correlation but not causation.
Bouchard’s analysis is the first to home in on organophosphate pesticides as a potential contributor to ADHD in young children. But the author stresses that her study uncovers only an association, not a direct causal link between pesticide exposure and ADHD. However, organophosphates are known to cause damage to nerve connections in the brain — after all that’s how they kill agricultural pests [TIME].
Still more to know. But another reminder to - wash your fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
Middle & High Schools
Starting time:
The American Academy of Pediatrics & Centers for Disease Control recommend classes should start at 8:30 a.m. of later.

Way to - Keep it Positive
Autism 
Autistic and normally developed children brains were scanned (MRI) as they were shown photos of facial expressions conveying a range of emotions (fear, happiness, anxiety, sadness, ...) and asked to perform a task.
Interesting patterns were observed in two areas. An area near the front of the brain that includes the mirror-neuron system (cells fire here both when an action is performed and when watching another person perform that action) and the movement center (An area associated with changing facial expressions).
Both groups of children had similar brain activity in the movement centers of the brain. However, the activity in the mirror-neuron centers was different. In fact the more severe a child's social impairment, the weaker the brain activity in the mirror-region.
Autistic children could make their face match the expression on the face in the picture, which supports the similar activity found in the movement center, but the weaker activity in the mirror-neuron area suggests they were not able to "feel what a person feels" when making a related facial expression.
Biophysically, these results can be explained since both the mirror-neuron center and the movement center are connected to the emotional centers of the brain. This connection creates empathy with other people.
Autistic children were able to distinguish facial expressions, copy them, but not feel or associate the particular emotion.
This suggests interventions that help children associate specific facial expression to past feelings they have experienced, which correspond to the expression pictured to facilitate children's emotional and social development.
More information
